Understanding the Concept of Quality of Life
Before delving into the reasons why there is a perceived lack of quality of life in India, it is important to understand what quality of life entails. Quality of life is a broad multidimensional concept that includes subjective evaluations of both positive and negative aspects of life. It goes beyond standard of living which is often equated with income. Instead, it looks at factors such as health, comfort, happiness, and ability to pursue personal goals.
Quality of life is not just about the availability of resources but also about the ability to enjoy life and feel satisfied. It demands a balance in all aspects of life, including physical, emotional, social, and spiritual. It is a subjective and dynamic concept that greatly varies from person to person and place to place. This is where the question arises - why is there no quality of life in India?
Overpopulation and Its Impact
One of the biggest problems facing India today is overpopulation. With a population of over 1.3 billion, India is the second most populated country in the world. Overpopulation leads to a host of problems, including overcrowding, lack of resources, and increased competition for jobs. This creates a challenging environment to improve or even maintain the quality of life.
Overpopulation also puts immense pressure on infrastructure, leading to inadequate access to clean water, proper sanitation, and healthcare. These are basic necessities, and without them, it becomes difficult to talk about quality of life. The problem is further exacerbated in urban areas, where slums are a common sight, reflecting the harsh realities of life for many Indians.
The Issue of Poverty
Poverty is another major factor that affects the quality of life in India. Despite the country's economic growth, poverty remains a persistent problem. According to World Bank data, over 20% of India's population lives below the international poverty line. Living in poverty means struggling for basic needs like food, shelter, and clothing.
Poverty also limits access to quality education and healthcare, two important determinants of quality of life. Without proper education, the cycle of poverty continues, with limited opportunities for income and advancement. Similarly, without access to quality healthcare, people's physical wellbeing is compromised, further diminishing their quality of life.
Gender Inequality and Discrimination
Gender inequality is another pressing issue that impacts the quality of life in India. Despite legal provisions for equal rights, gender discrimination is widespread, particularly in rural areas. Women face numerous challenges, from limited access to education and healthcare to gender-based violence and restrictions on their freedom.
Such discrimination not only affects the quality of life of women but also hampers the overall development of the country. Empowering women is crucial for improving the quality of life in India, as it leads to better health, education, and economic outcomes for the whole family.
Environmental Concerns
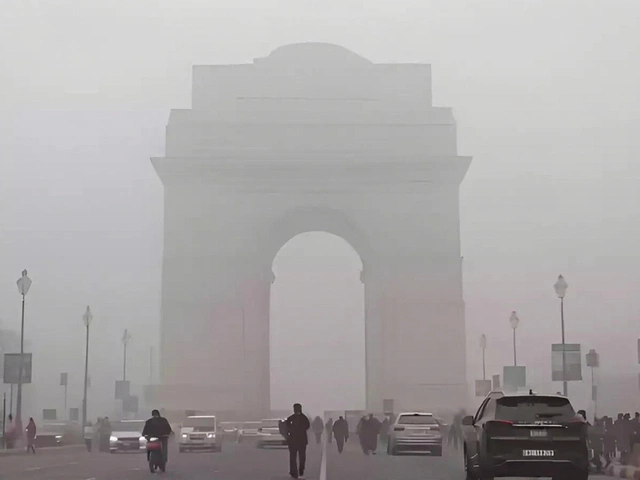
Environmental degradation is another factor that cannot be overlooked when discussing the quality of life in India. Rapid industrialization and urbanization have led to increased pollution, loss of biodiversity, and depletion of natural resources. The air quality in many Indian cities is among the worst in the world, posing serious health risks to the population.
Moreover, the country is highly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, with increasing instances of floods, droughts, and heatwaves. These environmental issues not only affect people's health but also their livelihoods, particularly in rural areas where people depend on agriculture and natural resources.
The Way Forward
Despite these challenges, it is important to note that the situation is not entirely bleak. There have been significant improvements in various aspects, such as the reduction in poverty rates and improvements in literacy rates. However, a lot more needs to be done to ensure a quality life for all Indians.
Addressing overpopulation through family planning, improving the quality of education and healthcare, promoting gender equality, and adopting sustainable practices are some of the strategies that can enhance the quality of life in India. It requires concerted efforts from the government, civil society, and individuals to make this a reality.